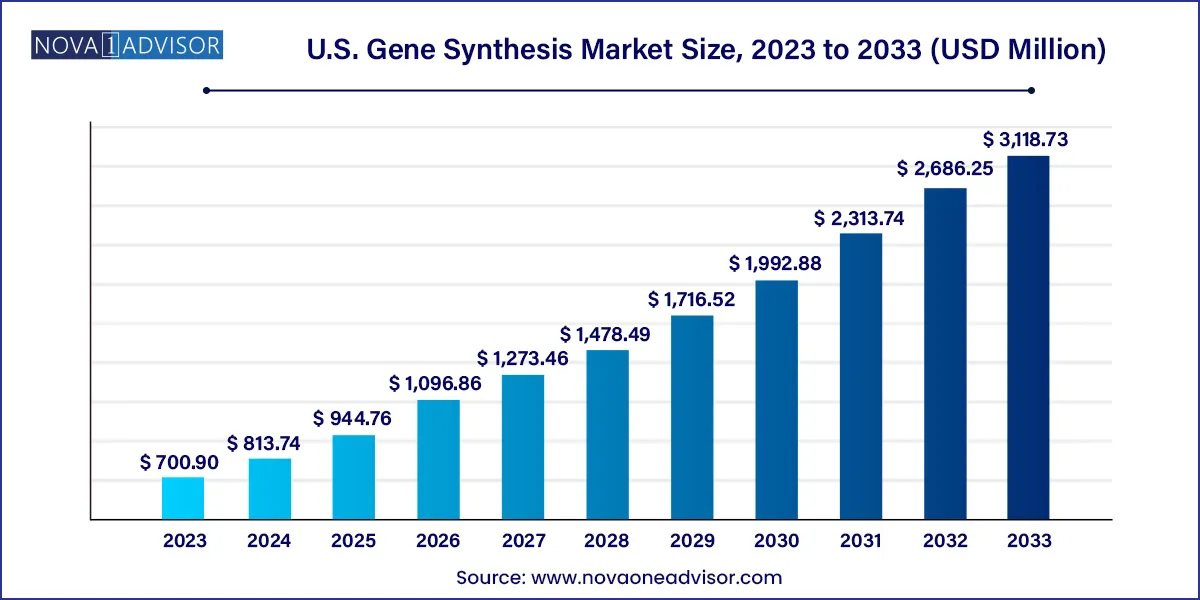
The U.S. Gene Synthesis market size was valued at USD 700.90 million in 2023 and is projected to surpass around USD 3,118.73 million by 2033, registering a CAGR of 16.1% over the forecast period of 2024 to 2033.
The U.S. gene synthesis market has evolved into a cornerstone of modern life sciences, biotechnology, and medical research. Gene synthesis refers to the artificial construction of genes in a laboratory setting, bypassing traditional DNA templates. This enables researchers and biotech firms to design and order genetic sequences tailored to specific research needs. The technology is widely utilized across applications such as synthetic biology, gene and cell therapy, vaccine development, diagnostics, and biopharmaceutical production.
Driven by the explosion of genetic information, declining costs of DNA sequencing and synthesis, and advances in automation, the gene synthesis market in the United States is growing rapidly. Increasing investments from pharmaceutical giants, the emergence of startups focusing on synthetic biology, and supportive government initiatives like the NIH's funding in genome research and the DARPA-led "Living Foundries" program have further stimulated market growth.
As synthetic biology gains ground in medicine, agriculture, and industrial biotechnology, gene synthesis stands out as an enabling technology. It allows for rapid prototyping of genes, construction of metabolic pathways, and even creation of entire synthetic organisms. The COVID-19 pandemic also spotlighted the technology's importance, as companies used synthesized genes to develop vaccines and diagnostics rapidly. This momentum continues, as researchers explore mRNA vaccine platforms, CRISPR tools, and on-demand genetic constructs for a range of diseases.
Adoption of High-throughput and Automated Platforms: Laboratory automation and high-throughput synthesis technologies are streamlining production and reducing human error.
Shift Toward Cloud-based Ordering and Delivery Systems: Companies like Twist Bioscience and GenScript offer online platforms that simplify custom DNA design and ordering.
Convergence with CRISPR and Gene Editing Tools: Synthesized genes are increasingly used as components in gene-editing experiments.
Customized Gene Libraries: Rapid demand is observed for tailor-made gene libraries for drug screening and pathway engineering.
Use of AI in Sequence Optimization: Artificial intelligence is improving codon optimization, expression levels, and synthesis efficiency.
Rise of Synthetic mRNA Applications: Demand for mRNA-based vaccines and therapeutics is driving gene synthesis needs.
Outsourcing to Specialized Providers: Pharma and biotech firms are increasingly outsourcing gene synthesis to reduce costs and focus on core R&D.
U.S. Gene Synthesis Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 813.74 million |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 3,118.73 million |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 16.1% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Method, services, application, end-use |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | GenScript; GENEWIZ; Boster Biological Technology; Twist Bioscience; ProteoGenix, Inc.; Biomatik; ProMab Biotechnologies, Inc.; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc.; OriGene Technologies, Inc. |
The explosive rise in gene and cell therapy pipelines is one of the major driving forces behind the U.S. gene synthesis market. These therapies, which involve modifying or inserting genes to treat or prevent diseases, require precise and reliable synthetic DNA sequences. Companies developing CAR-T cell therapies or CRISPR-based treatments often depend on gene synthesis services for producing guide RNAs, viral vectors, or other genetic payloads.
For instance, the success of FDA-approved therapies like Kymriah and Luxturna has demonstrated the clinical viability of gene-based interventions, leading to an uptick in both funding and clinical trials. These trials necessitate rapid and customizable gene synthesis, especially in the preclinical and scale-up phases. As regulatory bodies show increasing support for advanced therapies, the demand for high-quality, GMP-grade synthetic genes is expected to grow further.
Despite its promise, gene synthesis raises significant biosecurity and ethical challenges. The ability to synthesize any gene sequence, including those of pathogens, creates potential misuse scenarios. There are fears that malicious actors could produce synthetic versions of viruses or toxins, triggering biosecurity risks.
As a response, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has issued guidance on screening orders for synthetic DNA. Gene synthesis companies must now implement customer screening and sequence screening protocols. While these measures help safeguard public health, they also introduce regulatory burdens and additional costs, which may deter new market entrants and complicate cross-border collaborations.
The success of mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic revealed a significant opportunity for gene synthesis in rapid vaccine development. Gene synthesis allows scientists to recreate antigen sequences swiftly, enabling faster development cycles. Companies like Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech depended on synthesized genes to develop mRNA constructs encoding the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
Looking ahead, synthetic biology is expected to revolutionize vaccine development for other infectious diseases such as Zika, Ebola, and seasonal influenza. With rising public and private investments in vaccine research, the demand for rapid, reliable gene synthesis services will only grow. The possibility of developing universal flu vaccines or cancer immunotherapies via synthetic antigens offers new commercial avenues for gene synthesis providers.
Solid-phase synthesis dominated the U.S. gene synthesis market due to its long-standing use, established protocols, and high reliability for short to medium-length DNA sequences. This method enables the stepwise addition of nucleotides on a solid support, allowing for high control and accuracy. It is particularly effective for constructing oligonucleotides, primers, and gene fragments, which are then assembled into larger constructs. Its integration with automated synthesizers has made it the go-to method for many academic and biotech labs.
However, chip-based synthesis is anticipated to be the fastest growing method, thanks to its scalability and cost efficiency for large-scale projects. By utilizing microarray platforms, chip-based synthesis can produce thousands of sequences in parallel, significantly reducing the cost per base pair. This approach is particularly advantageous for constructing gene libraries or conducting multiplexed experiments in synthetic biology. Companies like Twist Bioscience are pioneering this segment by offering vast quantities of DNA at unprecedented speeds and affordability, which is driving adoption among pharma companies and synthetic biology startups.
Antibody DNA synthesis services held the largest share in the services segment, as monoclonal antibodies have become the backbone of many therapeutic and diagnostic strategies. Synthetic genes encoding variable regions, Fc fragments, or engineered antibodies are frequently produced to optimize therapeutic efficacy or reduce immunogenicity. With the rise in immuno-oncology and autoimmune therapies, demand for precise antibody DNA synthesis continues to climb. Additionally, companies working on bispecific antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates rely heavily on synthetic gene services for rapid prototyping.
Conversely, viral DNA synthesis services are gaining momentum, driven by their role in producing viral vectors used in gene therapies and vaccine development. The popularity of adeno-associated virus (AAV) and lentiviral vectors in clinical applications necessitates large-scale, error-free DNA templates. These sequences often involve repetitive and GC-rich regions, which pose challenges in traditional cloning—making synthetic DNA a preferable option. The trend is amplified by increasing FDA approvals for gene therapies utilizing viral vectors, stimulating market expansion.
Gene and cell therapy development emerged as the dominant application segment, primarily because synthetic genes are foundational to these cutting-edge treatments. From designing chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) for cancer treatment to engineering immune cells for rare genetic disorders, gene synthesis plays a crucial role. These applications require tailored sequences with optimized codons, specific promoters, and regulatory elements, all of which are best achieved through synthetic means. The clinical and commercial success of early therapies has catalyzed a wave of investment and R&D, solidifying this segment's leadership.
Vaccine development is projected to be the fastest growing application, especially in the wake of the pandemic. The ability to rapidly synthesize pathogen-specific genes for antigen presentation or mRNA platforms has proven invaluable. Emerging interest in therapeutic vaccines for cancer and chronic infections also highlights this segment's potential. Synthetic biology tools are increasingly being used to optimize vaccine stability, immunogenicity, and delivery, further increasing demand for gene synthesis as a core service in this domain.
Biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies dominate the end-use segment, owing to their expansive R&D pipelines, budget allocations, and regulatory compliance requirements. These companies frequently outsource gene synthesis for drug discovery, biologic development, and clinical trials. The synthetic production of therapeutic proteins, vaccines, and engineered cells is heavily dependent on the timely and accurate synthesis of genetic material. Partnerships between pharma companies and synthesis providers are also expanding, fostering innovation and scalability.
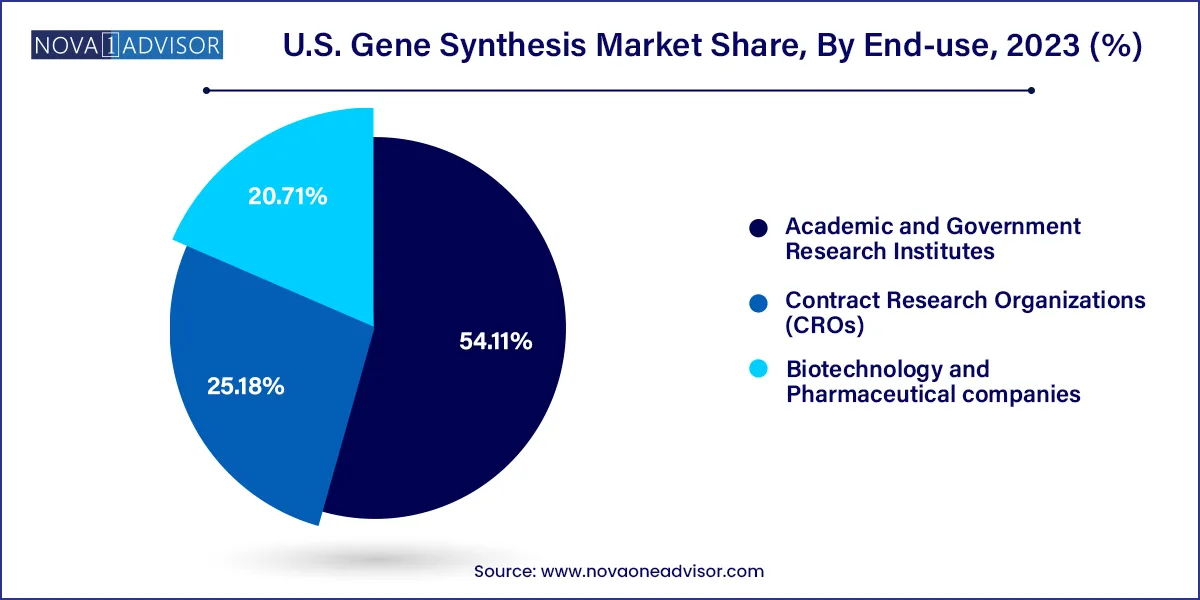
Meanwhile, academic and government research institutes represent the fastest growing end-user group, driven by increasing grants and collaborative research initiatives. Universities and national labs are leveraging synthetic DNA for fundamental research in genomics, epigenetics, and evolutionary biology. Programs such as iGEM (International Genetically Engineered Machine) and NIH-funded synthetic biology centers have boosted demand from educational institutions. Lower synthesis costs and user-friendly ordering platforms have made these services more accessible to academic researchers.
As the global leader in biotechnology and genomics, the United States is uniquely positioned to drive innovation in gene synthesis. The country hosts numerous biotech hubs such as Boston, San Diego, and the San Francisco Bay Area, where startups and established firms alike focus on synthetic biology, gene therapy, and molecular diagnostics. Federal initiatives like the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) and Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) provide both funding and regulatory frameworks that support gene synthesis R&D.
The U.S. also benefits from a strong academic network with institutions like MIT, Stanford, and Harvard actively involved in genetic engineering. These universities often collaborate with commercial entities, accelerating translation from research to application. Additionally, the FDA's progressive stance on advanced biologics and gene therapies offers a favorable regulatory environment. Venture capital funding for synthetic biology startups in the U.S. remains robust, creating fertile ground for innovation and market expansion.
March 2025: Twist Bioscience announced the expansion of its manufacturing facility in Oregon to meet the rising demand for chip-based gene synthesis services.
January 2025: GenScript USA launched a new AI-driven gene optimization tool designed to reduce synthesis errors and enhance expression efficiency.
November 2024: Thermo Fisher Scientific unveiled a collaboration with a leading mRNA therapeutics company to co-develop synthetic genes for vaccine production.
October 2024: Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT) introduced a new line of high-fidelity, long-length gene synthesis products tailored for viral vector production.
August 2024: Codex DNA received a significant NIH grant to develop on-demand gene synthesis solutions for pandemic preparedness.
Some of the key companies involved in gene therapy include Asklepios BioPharmaceuticals, CRISPR Therapeutics, Editas Medicine, Homology Medicines, Intellia Therapeutics, Pfizer, Passage Bio, Poseida Therapeutics, Sangamo Therapeutics, and Prevail Therapeutics, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; GenScript; and Brooks Automation, Inc, among others. Companies are expanding their global footprint by establishing collaborations, partnerships, and acquisitions to tap in new markets and countries. Collaborations with healthcare providers and research institutions, such as the Mayo Clinic and academic medical centers, are opportunistic to access expertise and assess their technologies.
U.S. Gene Synthesis Market Report Segmentation
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the U.S. Gene Synthesis market.
By Method
By Services
By Application
By End-use